How to calculate shrinkage in welding
What is shrinkage?
In a welded joint, expansion and contraction forces act on the weld metal and on the base metal. As the weld metal solidifies and fuses with the base metal, in this stage, it is in its maximum expanded form. While cooling, weld metal contract to the volume it would normally occupy at the room temperature, but it is restricted by the adjacent base metal. Because of this, stresses develop within the weld metal and the adjacent base metal.
A rough idea about shrinkage calculation is as under-Transverse shrinkage-
Fillet- 0.5 to 0.8mm per weld
Butt - 1 to 3mm per weld
Longitudinal shrinkage-
Fillet- 0.3%
Butt - 1.0%
How it affects Job, after welding?
Warping(distortion) of the base metal is caused by heat from the welding arc. distortion results from the expansion and contraction of the welding arc. distortion results from the expansion and contraction of the weld metal and adjacent metal during the welding process.
What precaution should we take to avoid shrinkage?
follow weld sequence
Keep shrinkage allowance during fit-up of job
use backstep welding
use peening during welding ( except root and final welding as it may lead to crack or can hide crack)
use strong back to support base metal during welding
use as few welds passes as possible
How to take advantage of shrinkage in a welded job.
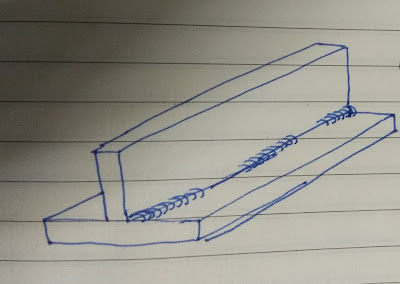
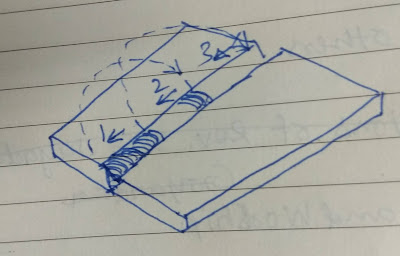
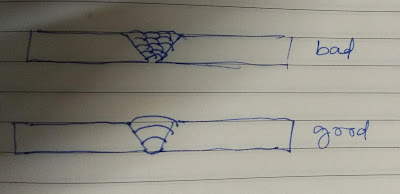
After welding an item sometimes it becomes out of a plane or not in a straight line, for correction a fitter does heat some area (see above pic) with his experience. By heating, steel expands and after cooling it shrinks little more to its original size causes pulling the item in the heating direction thus job(item) gets straighten.
Care must be taken during heating that heat should not exceed the recrystallization temperature of steel/material used or being heated.
Type of Distortion
Longitudinal distortion
Transverse distortion
Angular distortion
Twisting distortion
Bending distortion
Buckling distortion
Local distortion
Factors influencing distortion
Structurally related parameters
Material related parameters
Welding related parameters
Control of distortion
Before welding
Minimize welding
Edge preparation
Fillet size
Root gap control
Gas cutting
Strong backing
Preheating
supports
During welding
Backstep technique
Bach skip technique
Less number of passes
Weld sequencing
Weld axis to neutral axis distance
Intermittent welds
After welding
Mechanical correction
Pressing
Jacking
Heat correction